Y DNA haplogroup E Changed According to Surroundings!
Part of the Series:
DNA Types Changed According to Surroundings!
#3. YDNA HaploGroups E. Contents:
1. Extracts from Familypedia.
2. Extracts from Wikipedia.
3. Brit-Am Comments.
|
Brit-Am Discussion Group |
Contents by Subject |
Research Recognition Reconciliation Contribute |
|
Site Map Contents in Alphabetical Order |
This Site |
Haplogroups and Environment.
Correspondence of YHaplogroups to Specific Climes and Locations.
 |
1. Extracts from Familypedia
2. Extracts from Wikipedia
3. Brit-Am Comments.
1. Extracts from Familypedia
E (Y-DNA)
http://familypedia.wikia.com/wiki/Haplogroup_E_(Y-DNA)
Extracts:
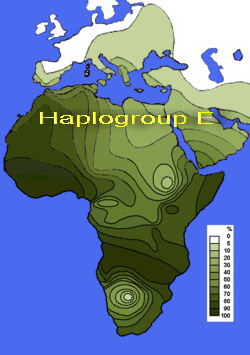
This haplogroup is found in Africa, the Middle East, and Europe. Haplogroup E is found in Africa, Asia and Europe and it is divided into three clades: E1 and E2 are found exclusively in Africa, while E3 is observed in Africa, Europe and western Asia. E3 is further divided into E3a and E3b, but only E3b is observed in significant frequency in Europe and western Asia in addition to Africa. ...[1] Most Sub-Saharan Africans belong to E(xE3b), while most non-Africans belong to the E3b clade of the E haplogroup.?
E1 (M33) headed for West Africa and today it is mainly present in the region of Mali.
E2 (M75) is present both in West and East Africa.
E3, by far the most frequent subbranch of E, diverged into two main subbranches E3a (M2) and E3b (M35) ... The bearers of E3a populated the coastal region of West Africa, where they largely mixed with indigenous Pygmy populations and gave birth to modern West Africans speaking languages of the Niger-Congo family. ... E3a is the most frequent Y-haplogroup in Sub-Saharan Africa today. It is also the most common Y-haplogroup among African American men.
Within eastern Africa, the haplogroup appears to be restricted to Ethiopia but E-M34 chromosomes have been found in a large majority of the populations from the Near East. E-M34 chromosomes from Ethiopia show lower variances than those from the Near East and appear closely related in the E-M34 network. Thus, it is assumed that E-M34 chromosomes were introduced into Ethiopia from the Near East.[2]
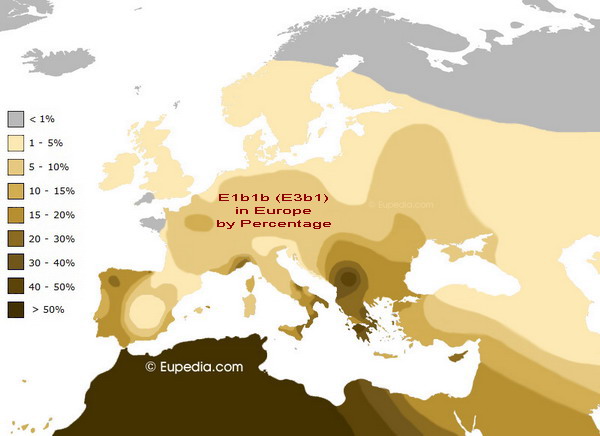
The subbranch E3b1 is present at high frequencies among the Greeks, Albanians, and South Italians (up to 25%), but its percentage gradually falls below 10% in the Carpathian basin and Iberia, and is negligible in other parts of Europe. Some E3b is instead explained by more recent genetic influence from North Africa.
 |
2. Extracts from Wikipedia
Haplogroup E (Y-DNA)
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Haplogroup_E_(Y-DNA)
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
In human genetics, Haplogroup E (M96) is a human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. Haplogroup E is one of the two main branches of the older Haplogroup DE, the other main branch being haplogroup D. The E clade is divided into two subclades: E1 (E-P147) and E2 (E-M75).
E is a clade of Haplogroup DE, with the other major clade, haplogroup D, being East Asian.
DE is a clade within M168 with the other two major clades, C and F, considered to have a Eurasian origin.
Haplogroup E (Y-DNA).
Most members of haplogroup E belong to one of its already identified subclades. E1a and E2 are found almost exclusively in Africa. E1b1a is the most prevalent subclade of E in Africa. It is observed at high frequencies in all African regions except the northernmost and easternmost portions of the continent. E1b1b is found at high frequencies in East Africa and North Africa and is the only subclade that is found in Europe and Asia at significant frequencies. E1b1b is common among Afro-Asiatic speakers in Africa as well as among Nilo-Saharan and Niger-Congo speakers in East Africa and Sudan. E1b1b is less common in West, Central, and Southern Africa, ...
The most basal lineages, paragroup E*, have been found in a single Bantu-speaking male from South Africa,[1] amongst pygmies and Bantus from the Cameroon/Gabon region,[14] and in two individuals from Saudi Arabia.[15]
While there have been no attested exemplars of E1*, its sub-clade, E1a (M33), is found most often in West Africa, and today it is especially common in the region of Mali. One study has found haplogroup E1a-M33 Y-chromosomes in as much as 34% (15/44) of a sample of Malian men. Haplogroup E1a also has been detected among samples obtained from Guinea-Bissau,[10] Moroccan Berbers, Sahrawis, Burkina Faso, northern Cameroon, Senegal, Sudan, Egypt, Calabria (including both Italian speakers at 1.3% and Albanian speakers at 2.9%), Trentino (1/67 or 1.5%),[16] and Portugal (5/553 or approximately 0.9%).[2][13][17]
Haplogroup E1a has been detected in North Africa and Europe independently of the ubiquitous E1b1a. Because E1b1a is known to have expanded recently, this leaves open the possibility of an ancient expansion from West Africa into North Africa and Europe of E1a lineages.[17]
E1b1, also known as E-P2 or E-PN2, includes the majority of all E lineages existing today. There are no known basal E1b1*.
Today there are two main surviving branches of this haplogroup, E1b1b (E-M215) and E1b1a (E-V38).
E1b1a is the primary subclade of E in West Africans and many populations of Central, Eastern, and Southern Africa. It is observed in lower frequencies in North Africa and parts of West Asia. E1b1a has several subclades but many members of E1b1a subclades are either E1b1a1f (E-U186) or E1b1a1g (E-U175).
E1b1b is at once the most common E subclade amongst East African Maasai, Somalis, Ethiopians, Eritreans and North African Sudanese, Egyptians, Berbers and Arabs. It is also common in West Asia, from where it spread into the Balkans and the rest of Europe. E1b1b has at least four common subclades: E1b1b1a (E-V68), E1b1b1b (E-V257), E1b1b1c (E-M123), and E1b1b1e (E-M293), the last of which spreads from Ethiopia to South Africa.
Main article: Haplogroup E2 (Y-DNA)
E2 (M75) is present throughout Sub-Saharan Africa, in East Africa, Southern Africa, Central Africa, and West Africa. The highest concentration of haplogroup E2 has been found among South African and Kenyan Bantus, with moderate frequencies of this haplogroup being observed in samples from Burkina Faso, Cameroon, Gabon, Hutu and Tutsi from Rwanda, Malagasy from Madagascar, Fon from Benin, Iraqw from Tanzania,[18] South African Khoisan, Sudan, and Senegal, as well as small frequencies in samples obtained from Qatar, Oman, Ethiopian Oromo, and Somali immigrants to Denmark.
 |
3. Brit-Am Comments.
All of the above might look a bit complicated but apart from the long names and the different names meaning the same things it is not so.
On the whole E belongs to Africa.
Most is E1b. Other (earlier?) types are too few to be overduly specific but seem to all pertain to Africa.
Those (i.e. non-E1b E subtypes) found in Sicily etc probably also came from Africa. They have mixed in so heavily with females from other regions that little for certain may be said about them.
E1b is split into 2 major groups:
E1b1a (also known as E3a) are mainly African, negroid peoples.
E1b1b (also known as E3b1) are found in North Africa and Southern Europe.
E3b1 are mainly white-types except in Central and Eastern Africa (Maasai, Somalis, Ethiopians, etc) where they have dark to light skins but mainly "European"-type features.
For Dark Africa the E3a type more or less corresponds with geographical regions, sub-equatorial savannah type vegetation more than jungle, allowing for an historical wide range of movement and intermixtures.
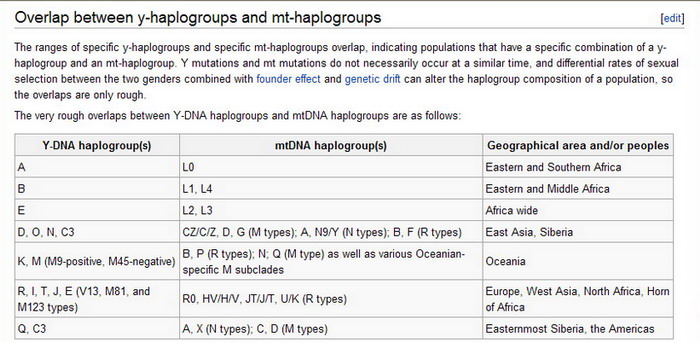
The female of E3a is L2, and L3 which is related to L0, L1, L4 found amongst Bushman (Khoisan) and Pygmies.
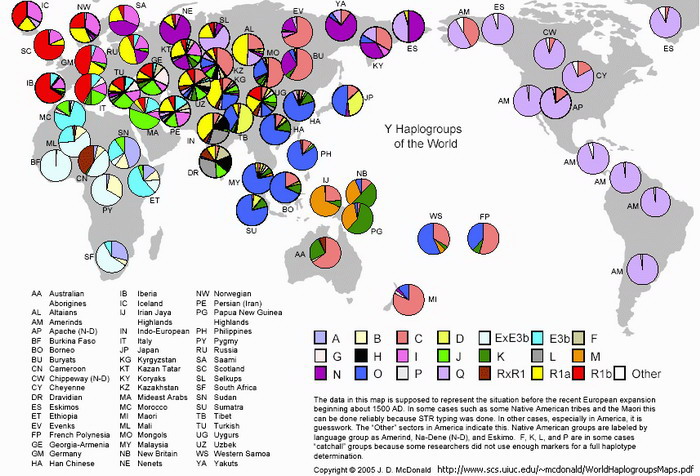
On the map of Y haplogroups by J.D. MacDonald:
E3a is called EXE3b (color = light cyan-blue);
E3b1 is called E3b (color = dark cyan-blue);
In short we see from the above that E is divided into 2 main types: An African specific type and a North African-South European type.
The African E3a overlaps geographical areas and climates.
In Africa different types of E3a correspond to changes in climate and environment and pertain to physical types suited to their environment.
They are contiguous with each other and in most areas where found are the dominant element.
It should also be noted that the strong presence of E3a in South Africa may be relatively recent (i.e. within the last few centuries) due to the migration of Bantu-speaking peoples southward.
The correspondence of E3a with specific regions and environment etc and even the differentiations reflecting changes in the surroundings will be admitted by most since this is quite obvious.
It is the "white" type (E3b1) and its presence in both hot and cold environments that has been used to counter our claims that YDNA haplogroups reflect environmental influence.
We will discuss E3b1 in the next article.
 |
TO BE CONTINUED!
See Also:
Y DNA "Evolutionary" Sequence Reversed!
YDNA Haplogroups Determined by Climate!

Pleased with what you read'
Click Here to make an offering. |
'It is impossible to rightly govern the world without
God or the Bible.'
George Washington
Brit-Am is the "still small voice" that contains the truth.
"after the earthquake a fire, but the LORD was not in the fire; and after the fire a still small voice"
[1-Kings 19:12].
 |
 |